Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit shows a SAF Forwarder configuration attached to a Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
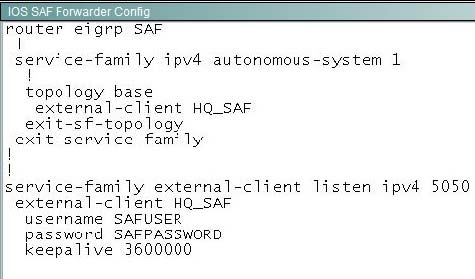
Which minimum configuration for a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express SAF Forwarder is needed to establish a SAF neighbor relationship with this SAF Forwarder?
A. router eigrp SAF
i
service-family ipv4 autonomous-system 1
!
topology base
exit-sf-topology
exit-service-family
voice service saf
profile trunkroute 1
session protocol sip interface Loopback1 transport tcp port 5060 !
B. router eigrp SAF
!
service-family ipv4 autonomous-system 1
!
topology base
exit-sf-topology
exit- service-family
!
voice service saf
profile trunk-route 1
session protocol sip interface Loopback1 transport tcp port 5060
!
profile dn-block 1 alias-prefix 1972555
pattern 1 type extension 4xxx
!
profile callcontrol 1
dn-service
trunk-route 1
dn-block 1
dn-block 2
!
channel 1 vrouter SAF asystem 1
subscribe callcontrol wildcarded
publish callcontrol 1
!
C. router eigrp SAF
!
service-family ipv4 autonomous-system 1
!
topology base
exit-sf-topology
exit-service-family
!
D. None of above configurations contain sufficient information.


I’m not sure if answer C refers to a Local Neighbor.
The following terms are used when describing neighbor types:
• Local Neighbor–A neighbor that is adjacent on a shared subnet (or common subnet) and uses a link-local
multicast address for packet exchange. This is the default type of neighbor in Cisco SAF.
• Static Neighbor–Any neighbor that uses unicast to communicate, is one hop away, is on a common
subnet, and whose IP address has been specified using the neighborip-address command.
• Remote Neighbor–Any neighbor that is multiple hops away, including Remote Static Neighbors.
• Remote Static Neighbor–Any neighbor that uses unicast to communicate, is multiple hops away, and
whose IP address has been specified using the neighborip-address command.
• Remote Multicast-Group–Any neighbor that is multiple hops away, but does not have its IP address
manually configured using the neighborip-address command, and uses a configured multicast group
address for packet exchange.
• Remote Unicast-listen (or simply Unicast-listen)–Any neighbor that uses unicast to communicate, is
multiple hops away, and whose IP address has not been configured using the neighborip-address
command.
Answer is C
For multicast dyn neighbor – the MINIMUM config is c!
Flimsy is pointing to static neighbors.
Answer Should be D
A , B &C are not having any neighbor command provied
Use the following commands to configure static neighbor adjacencies between Cisco SAF Forwarders.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. router eigrp virtual-instance-name
4. service-family {ipv4 | ipv6} [vrf vrf-name] autonomous-system autonomous-system-number
5. neighbor {ip-address {interface-type interface-number} | description word | maximum-service} | maximum-service number [threshold-value] [dampened | reset-time | restart interval | restart-count | warning-only]}
6. exit-service-family