Refer to the exhibit.
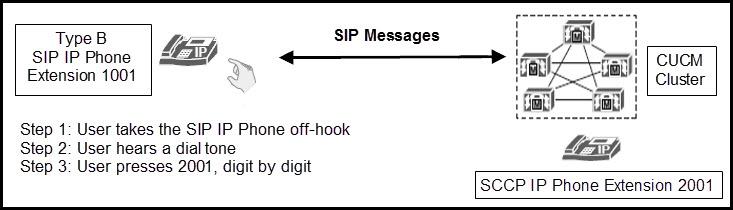
A user is going through a series of dialing steps on a SIP Type B IP phone (for example, a Cisco 7975) to call an SCCP IP phone. Both phones are registered to the same Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster. Assuming the calling SIP phone is associated with a SIP dial rule with a pattern value of 2001, which statement about how digits are forwarded to Cisco Unified Communications Manager for further call processing is true?
A. As each digit is pressed on the SIP IP phone, it is sent to Cisco Unified Communications Manager in a SIP NOTIFY message as a KPML event.
B. The SIP IP phone will wait for the interdigit timer to expire, and then send each digit to Cisco Unified Communications Manager as a separate KPML event in a SIP NOTIFY message.
C. The SIP IP phone will wait for the interdigit timer to expire, or for the Dial softkey to be selected before sending all digits to Cisco Unified Communications Manager in a SIP INVITE message.
D. The SIP IP phone will wait for the interdigit timer to expire, or for the Dial softkey to be selected before sending the first digit in a SIP INVITE and the subsequent digits in SIP INFORMATION messages.
E. The SIP IP phone will wait for the interdigit timer to expire, and then send all digits to Cisco Unified Communications Manager in a SIP INVITE message.


E is definitely the closest.
I don’t really think the user should have to wait for the inter-digit timeout since we have a matching SIP Dial Rule (2001). I would think that all digits would be sent to CUCM in a SIP INVITE message as soon as 2,0,0,1 were dialed, without having to wait for the inter-digit timeout, since there’s a SIP Dial Rule.
In my opinion, none of these are correct.. but E is definitely the closest.
Note As soon as SIP dial rules are implemented on Type-B IP phones, KPML-based dialing is disabled. If a user dials a string of digits that do not match a SIP dial rule, none of the individual digit events will be relayed to Unified CM. Instead, the entire dialed string will be sent en-bloc to Unified CM once the dialing is complete (That is, once inter-digit timeout has occurred).
Type-B phones using SIP dial rules offer only one way to dial patterns not explicitly configured on the phone. If a dialed pattern does not match a SIP dial rule, the user has to wait for inter-digit timeout before the SIP NOTIFY message is sent to Unified CM.
7975 Phone doesn’t need the interdigit timer since it support KPML. My answer is A.